Uric acid is a compound composed of nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen with a chemical formula C5H4N4O3. It is the resultant of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides. Uric acid is a normal component of urine. The IUPAC name of uric acid is 7,9-Dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione and the other names are 2,6,8-Trioxypurine, 2,6,8-Trioxopurine; 1H-Purine-2,6,8-triol. Acidity and basicity of uric acid are 5.6 and 8.4 respectively. In this short piece of article, learn more about the uric acid formula, its properties along with its chemical structure and its clinical significance.
Uric Acid Properties
| Properties of Uric Acid | |
| Name | Uric Acid |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Chemical Formula | C5H4N4O3 |
| Melting Point | 300 °C |
| Density | 1.87 g/cm³ |
| Molar Mass | 168.1103 g/mol |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble in Water |
Uric Acid Chemical Structure
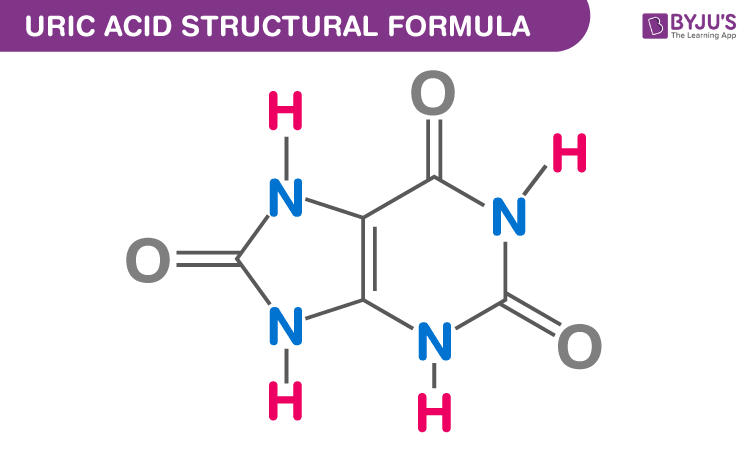
Clinical Significance of Uric Acid
- High levels of uric acid in the human body may induce Gout. Gout is a painful condition in capillaries, joints and skin resulting due to the precipitation of needle-like crystal of uric acid in these areas.
- Low levels of uric acid result in a number of neurological disorders including multiple sclerosis.
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments